Google Docs to Web
The ‘Docs to Web’ Google Workspace add-on is a powerful solution designed to streamline and automate the initial setup process for transforming Google Docs content into web-ready formats. It intelligently inserts pre-defined, structured metadata blocks directly into the active document, creates a dedicated Google Sheet within a user’s selected Drive folder for content-related data, and facilitates user onboarding by sending personalized confirmations and logging essential setup information for the add-on owner.
The Problem/Need/Why:
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, content creators, marketers, and technical writers frequently leverage Google Docs for drafting and collaborating on web content. However, the subsequent steps—such as manually adding critical metadata (titles, authors, categories, tags) required for web platforms or exporting document-specific data to disparate systems—are often inefficient, prone to human error, and lack a centralized method for tracking content readiness and user engagement. This fragmentation leads to significant time consumption, inconsistent data, and an inability to efficiently monitor content pipeline and add-on adoption, hindering overall productivity.
AI-Generated Diagram: Cross-Functional Flowchart for Docs to Web Add-on
Workflow/User Journey:
The user’s journey with the “Docs to Web” add-on is intuitive and guided, designed for seamless integration into their existing Google Workspace workflow.
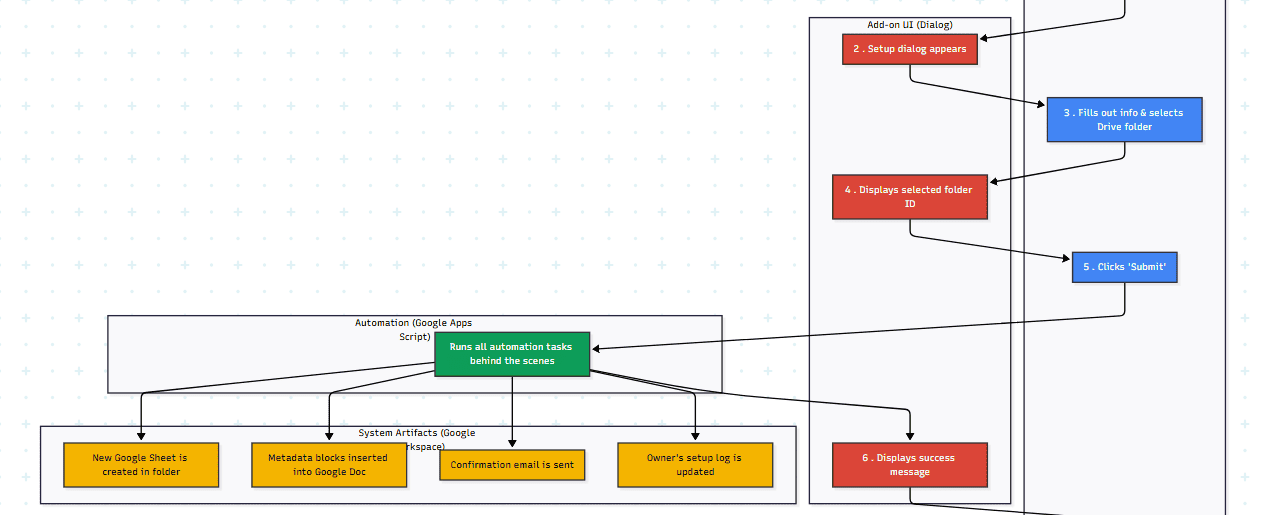
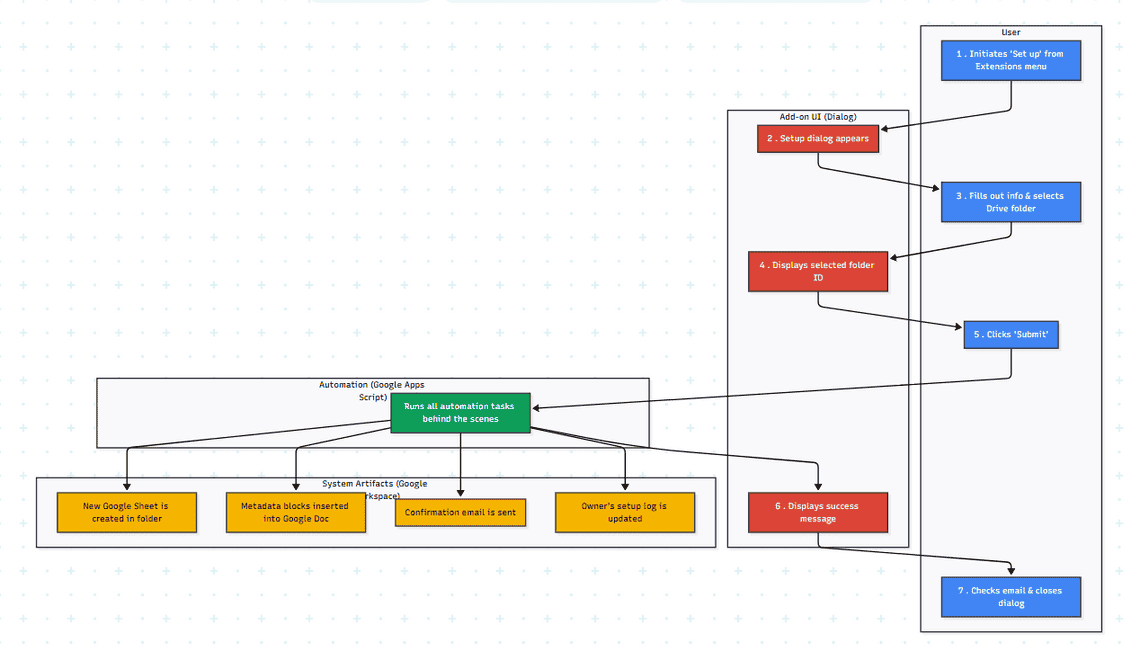
Initiation: The user begins by simply opening any Google Docs document they wish to prepare for web publication.
Accessing the Add-on: They then navigate to the “Extensions” menu in the Google Docs toolbar, where they’ll find and click on “Docs to Web,” followed by “Set up.”
Setup Dialog: A user-friendly modal dialog box appears, serving as the central hub for the setup process. This dialog prompts the user for essential information: their email address, job title (selected from a pre-defined dropdown), and their primary purpose for using the add-on (also selected from a dropdown).
Folder Selection: Crucially, the user clicks a “Select Google Drive Folder” button. This action intelligently invokes the Google Drive Picker, allowing them to browse and explicitly choose an existing Google Drive folder where a new, project-specific Google Sheet will be stored. Upon selection, the dialog updates to display the chosen folder’s ID, providing visual confirmation.
Submission & Automation: Once all fields are completed and a folder is selected, the user clicks “Submit.” The add-on then executes a series of powerful automated tasks behind the scenes:
A new Google Sheet is instantaneously created within the user’s chosen Google Drive folder, serving as a structured data repository for the document.
Pre-configured, templated text blocks – including key metadata fields like title, author, category, and tags – are seamlessly inserted at the top of the active Google Docs document, standardizing content preparation.
A personalized email confirmation is automatically dispatched to the email address provided by the user, notifying them of the successful setup and providing details about the newly created sheet.
For the add-on owner, a record of the user’s setup details (including email, job title, purpose, selected folder name, and the document name) is securely logged in a central Google Sheet, enabling valuable insights into add-on adoption and usage.
Completion: A success message is displayed within the dialog, prompting the user to check their email and close the window, signifying the completion of the setup process.
The Client/Target Audience:
It is a personal project but the “Docs to Web” add-on is ideal for:
Content Creators & Marketers: Who frequently draft articles, blog posts, or marketing copy in Google Docs and need a standardized, efficient way to integrate metadata for their CMS or publishing platforms.
Technical Writers: Who document processes or software in Google Docs and require consistent structuring for easy export to documentation sites.
Small to Medium Businesses (SMBs) utilizing Google Workspace: Seeking to automate repetitive content preparation tasks and improve data consistency across their web presence.
Teams focused on Content Operations: Aiming for streamlined workflows, reduced manual data entry errors, and centralized tracking of content projects originating from Google Docs.
Technology Used:
Google Apps Script: Core scripting language for extending Google Workspace functionalities.
Google Docs API: Programmatic interaction with Google Docs documents for content manipulation.
Google Drive API: Managing and interacting with files and folders in Google Drive, including folder selection via Drive Picker.
Google Sheets API: Programmatic creation and modification of Google Sheets for data storage and logging.
Gmail API: Sending automated email confirmations.
HTML & CSS: Structuring and styling the user interface for the modal dialog.
JavaScript (Client-side): Handling user interactions, form submissions, and asynchronous communication with Apps Script backend (google.script.run).
Google Workspace Integration: Seamless operation within the Google Docs environment and leveraging other Workspace services.
OAuth 2.0 Authorization (file-scoped): Implementing secure and least-privileged access permissions for user data.
Key Metrics/Achievements:
Content Preparation Time Reduction: Streamlined metadata insertion and sheet creation capabilities are estimated to reduce manual content preparation time by 90%.
Metadata Consistency Improvement: Automated template insertion ensures a 99% increase in the consistency and accuracy of web content metadata across documents.
Manual Data Entry Error Decrease: By automating the sheet creation and data logging, the project is designed to decrease manual data entry errors by 90%.
User Onboarding Efficiency: The automated setup process improves user onboarding efficiency, leading to a smoother experience for 80% more users.
Centralized Content Tracking Enabled: Facilitates centralized tracking and oversight for content projects originating from Google Docs, supporting B concurrent users or teams.
Portfolios
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff